Welcome to the Ansible_Workshop
Welcome to the Ansible_Workshop
The primary objective of this workshop is to provide an in-depth introduction to Ansible and the associated tools essential for playbook development within the Ansible framework. Throughout this workshop, we will guide you through the process of installing Python packages, with a particular focus on Ansible, and subsequently, we will delve into the intricacies of crafting playbooks and deploying configurations to network routers and switches.
Our ultimate goal during this workshop is to equip participants with the knowledge and skills required to construct playbooks that facilitate the deployment of our standardized office infrastructure. Below, you will find a schematic representation of the physical network connectivity within each pod for reference. 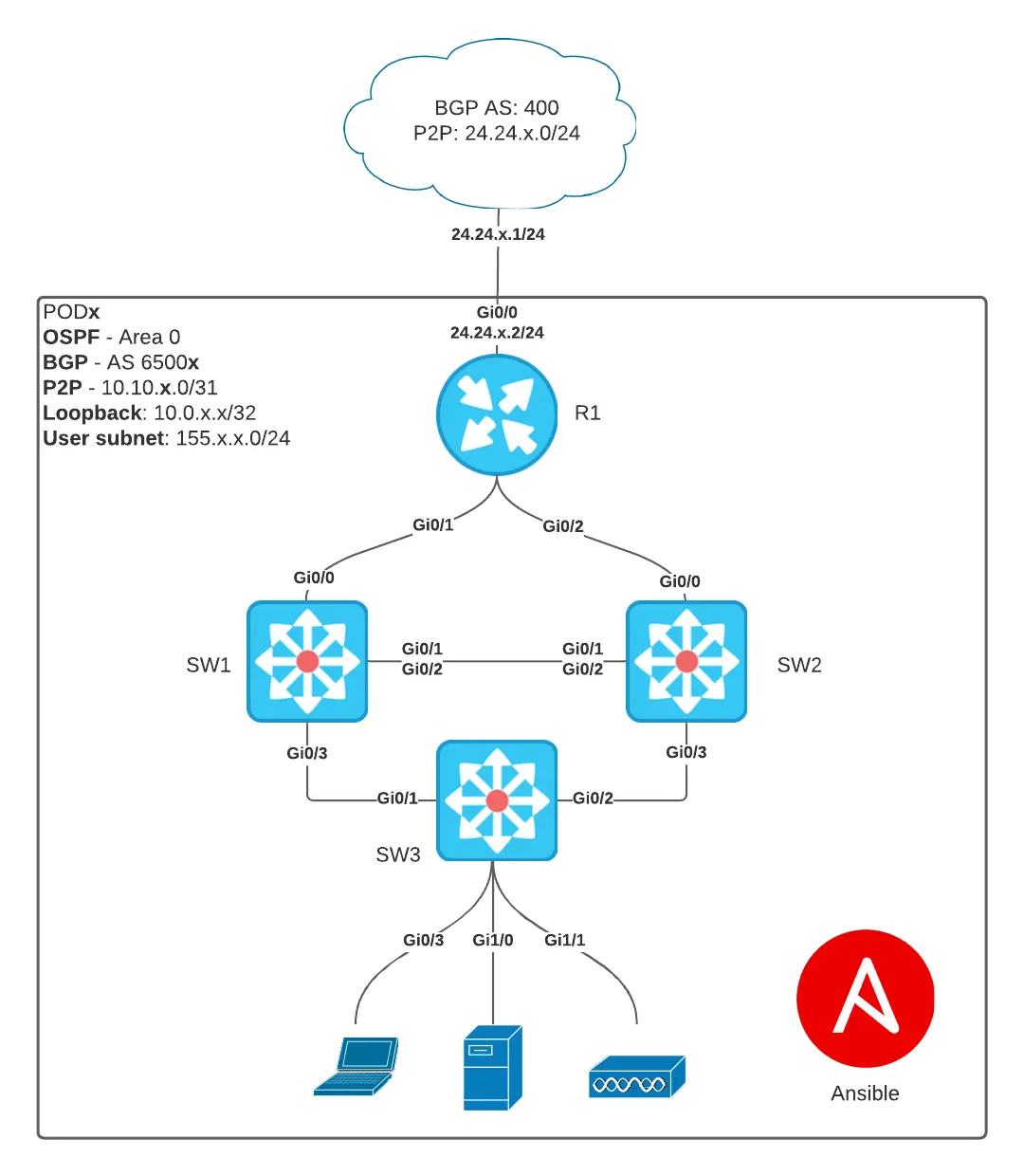 Using the diagram above as a reference we have several tasks that need to be completed before we can call our deployment completed.
Using the diagram above as a reference we have several tasks that need to be completed before we can call our deployment completed.
- (1) Access switch
- Configure the following vlans:
- Users - Vlan 300
- Servers - Vlan 350
- Guests - Vlan 400
- Native Vlan - Vlan 666
- Configure the following Access ports:
- Users - Port Gi0/3
- Servers - Port Gi1/0
- Guests - Port Gi1/1
- Configure a Layer 2 trunk to core switch 1 and core switch 2 on the Ports Gi0/1 and Gi0/2
- Trunks should only pass the configured vlans
- A linux VM has been connect to port Gi0/3 on the access switch and is accessible from the Guacamole front end
- Configure the following vlans:
- (2) Core switches
- Configure the following vlans:
- Users - Vlan 300
- Servers - Vlan 350
- Guests - Vlan 400
- Native Vlan - Vlan 666
- Configure Layer 2 trunk ports to the access switch on ports Gi0/3
- Trunks should only pass the configured vlans
- Configure a Layer 2 port channel between both core switches on Ports Gi0/1 and Gi0/2
- Trunks should only pass the configured vlans
- Use Port-Channel 12
- Configure SVIs for the following:
- Users - IP 155.x.1.0/26
- Servers - IP 155.x.1.64/26
- Guest - IP 155.x.1.128/26
- Configure VRRP protocol for redundancy on above vlans
- Use the first IP in the scope as your gateway
- Configure Layer 3 interfaces as UPLINKS to the router
- Core Switch 1 Port Gi0/0 with IP 10.x0.1.1/31
- Core Switch 2 Port Gi0/0 with IP 10.x0.1.3/31
- Configure Loopback0 interface to facilitate iBGP protocol peering
- Core Switch 1 Loopback0 IP 10.x.1.2/32
- Core Switch 2 Loopback0 IP 10.x.1.3/32
- Configure OSPF to facilitate iBGP Loopback0 peering
- Use iBGP to advertise Users, Servers, and Guest subnets to the router
- Use AS 6500x
- Configure the following vlans:
- (1) Router
- Configure Layer 3 interfaces as DOWNLINKS to both core switches
- Port Gi0/1 to Core Switch 1 with IP 10.x0.1.0/31
- Port Gi0/2 to Core Switch 2 with IP 10.x0.1.2/31
- Configure Loopback0 interface to facilitate iBGP protocol
- IP 10.x.1.1/32
- Configure OSPF to facilitate iBGP protocol
- Configure iBGP receive advertised Users, Servers, and Guest subnets from the core switches
- Use AS 6500x
- Configure Port Gi0/0 with IP 24.24.x.2/24
- The ISP ASN is 400 and the ISP IP address will be 24.24.x.1
- Configure eBGP to advertise and Aggregate subnet from the Users, Servers, and Guest subnets
- Accept a default route from the ISP
- Configure DHCP server for the Users, Servers, and Guest subnets
- Configure Layer 3 interfaces as DOWNLINKS to both core switches
The Lab diagram above consists of the IP addressing for each POD. The (x) will be replaced with the POD number you are using. This workshop has been broken down into separate sections covering everything from installing and using VSCode to building Ansible playbooks and Jinja templates.
